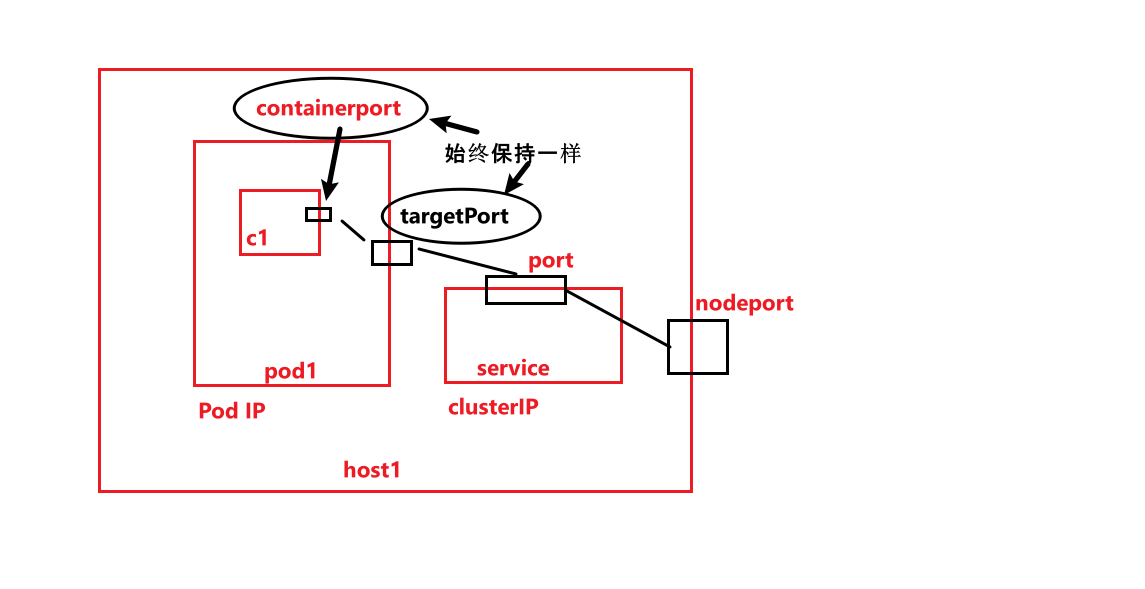
本文会通过container中的应用的几种访问方式来解释containerPort, targetPort, port, nodePort的关系和区别。
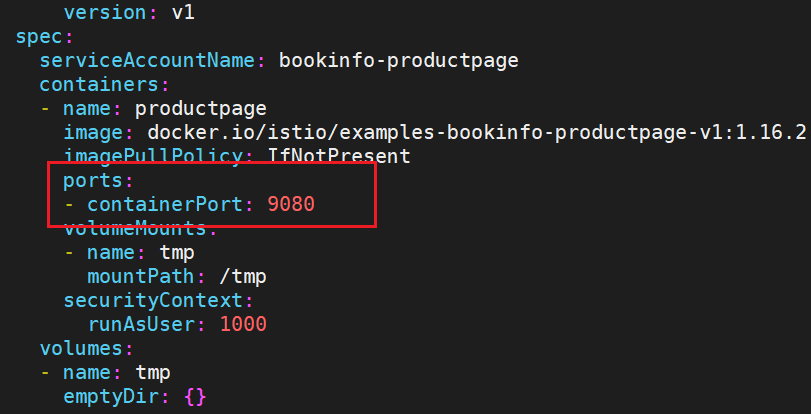
containerPort 容器暴露的端口,在container spec里声明。
可以通过podIP:containerPort来访问容器内应用。
1 2 3 4 $ k get pod -owide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE pod1 2/2 Running 0 133m 192.168.227.89 otcloud-node1 pod2 2/2 Running 0 47m 192.168.227.97 otcloud-node1
1 2 # 可以访问容器内应用 curl 192.168.227.97:9080
Notes:
如果一个pod里声明了多个容器,那么每个容器暴露的端口必须不同,否则容器启动会失败。(Address already in use)
更进一步 ,因为一个pod里的所有容器都共享网络namespace,所以它们共享IP,和端口。
targetPort 是Service 资源里的一个概念,在service的声明中使用。
targetPort是Pod上的端口,从port/nodePort上来的数据,经过kube-proxy流入到后端pod的targetPort上,最后进入容器。
如果不指明targetPort,默认targetPort和service暴露的port一致。
下面是一个service的声明:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: productpage labels: app: productpage service: productpage spec: ports: - port: 9999 name: http selector: app: productpage
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 k describe svc productpage Name: productpage Namespace: default Labels: app=productpage service=productpage Annotations: <none> Selector: app=productpage Type: ClusterIP IP Families: <none> IP: 10.97.239.58 IPs: 10.97.239.58 Port: http 9999/TCP TargetPort: 9999/TCP # 9999 和上面container暴露的接口不一致,访问一定会失败 Endpoints: 192.168.227.97:9999 Session Affinity: None Events: <none>
解决方法:
显式地声明targetPort: 9080
使用9080作为port,这样targetport也是9080,就可以和container port连接起来。
这里我们把targetPort显式的写成9080,会得到:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 k describe svc productpage Name: productpage Namespace: default Labels: app=productpage service=productpage Annotations: <none> Selector: app=productpage Type: ClusterIP IP Families: <none> IP: 10.97.239.58 # cluster IP! IPs: 10.97.239.58 Port: http 9999/TCP # 注意! TargetPort: 9080/TCP # 注意! Endpoints: 192.168.227.97:9080 # 注意! Session Affinity: None Events: <none>
这个service的细节要好好研究一下。
IP: Service的cluster IP。
Port: Service的cluster IP暴露的接口。
TargetPort: 容器暴露的接口。
Endpoint: podIP:targetPort,注意这里是targetPort,不是containerPort。
又有访问容器内应用的新方式:
1 2 3 4 5 # clusterIP:port curl 10.97.239.58:9999 # by endpoint, 跟containerPort里讲到的实际是一样的 curl 192.168.227.97:9080
Port 上面讲的差不多了,也是service 里的概念,是指在clusterIP上暴露的端口,是一个虚拟的东西。
clusterIP:虚拟的IP,在集群内可以相互访问。它只是存在service的规则当中。 注意,它不是podIP。
nodePort nodePort 提供了集群外 部客户端访问 Service 的一种方式,nodePort 提供了集群外部客户端访问 Service 的端口,通过 nodeIP:nodePort 提供了外部流量访问k8s集群中service的入口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 $ k get svc -owide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR productpage NodePort 10.97.239.58 <none> 9999:30066/TCP 25m app=productpage $ k describe svc productpage Name: productpage Namespace: default Labels: app=productpage service=productpage Annotations: <none> Selector: app=productpage Type: NodePort IP Families: <none> IP: 10.97.239.58 IPs: 10.97.239.58 Port: http 9999/TCP TargetPort: 9080/TCP NodePort: http 30066/TCP # 在host node上暴露的端口 Endpoints: 192.168.227.97:9080 Session Affinity: None External Traffic Policy: Cluster Events: <none>
又一种新的访问方式:
1 2 # hostIP:nodeport curl localhost:30066
总结:
三种访问方式以及范围:
方式
范围
podIP:targetPort
和pod在同一个网络下
clusterIP:port
在集群中
hostIP:nodeport
主机之间也可以访问